Hello Students! Are you searching for MCQ questions for NEET exam? You are in the right place.
JEET MCQ offers mcq questions on all chapters of all subjects that are a part of NEET syllabus.
For chapter-wise MCQ questions, visit the following links:
In this article, we have posted 50 questions from equilibrium chapter from chemistry. These questions will be your ultimate source for your revision. We have also provided answer key and detailed solution so that there is no doubt left in your mind. Good Luck!
Equilibrium MCQ Questions for NEET
Question 1-25
1. Which may be added to one litre of water to act as a buffer?
a) One mole of HC2H3O2 and one mole of HCl
b) One mole of NH4OH and one mole of NaOH
c) One mole of NH4Cl and one mole of HCl
d) One mole of HC2H3O2 and 0.5 mole of NaOH
2. An aqueous solution of 1 M NaCl and 1 M HCl is
a) not a buffer but pH < 7
b) not a buffer but pH > 7
c) a buffer with pH < 7
d) a buffer with pH > 7
3. In the following reversible reaction,
2 SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2 SO3 + Q cal
Most suitable condition for the higher production of SO3 is
a) Low temperature and high pressure
b) Low temperature and low pressure
c) High temperature and high pressure
d) High temperature and low pressure
4. Select the pKa value of the strongest acid from the following
a) 1.0
b) 3.0
c) 2.0
d) 4.5
5. The pH of a 0.1 M solution of NH4OH (having Kb=1.0×10-5) is equal to
a) 10
b) 6
c) 11
d) 12
6. In the reaction, H2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ 2 HCl(g)
a) Kp ≠ Kc
b) Kp = Kc
c) Kp > Kc
d) Kp &It; kc
7. The total number of different kind of buffers obtained during the titration of H3 PO4 with NaOH are:
a) 3
b) 1
c) 2
d) Zero
8. Which will not affect the degree of ionisation?
a) Temperature
b) Concentration
c) Type of solvent
d) Current
9. Which of the following has highest pH?
a) M/4 KOH
b) M/4 NaOH
c) M/4 NH4OH
d) M/4 Ca(OH)2
10. Solubility product constant [Ksp] of salts of types MX, MX2 and M3 X at temperature ‘T’ are 4.0×10-8, 3.2×10-14 and 2.7×10-15respectively. Solubilities (mol, dm-3) of the salts at temperature ‘T’ are in the order
a) MX>MX2>M3 X
b) M3 X>MX2>MX
c) MX2>M3 X>MX
d) MX>M3 X>MX2
11. Which of the following base is weakest?
a) NH4OH; Kb = 1.6×10-6
b) C6 H5 NH2; Kb = 3.8×10-10
c) C2H5NH2; Kb = 5.6×10-4
d) C9H7N; Kb = 6.3×10-10
12. One litre of water contains 10-7 mole H+ ions. Degree of ionisation of water is:
a) 1.8×10-7%
b) 1.8×10-9%
c) 3.6×10-7%
d) 3.6×10-9%
13. A precipitate is formed when
a) The ionic product is nearly equal to the solubility product
b) A solution becomes saturated
c) The ionic product exceeds the solubility product
d) The ionic product is less than solubility product
14. The precipitation is noticed when an aqueous solution of HCl is added to an aqueous solution of:
a) NaNO2
b) Ba(NO3)2
c) ZnSO4
d) HgNO3
15. Which of the following is not a Lewis base?
a) NH3
b) H2O
c) AlCl3
d) None of these
16. Solubility of BaF2 in a solution of Ba(NO3)2 will be represented by the concentration term
a) [Ba2+]
b) [F-]
c) 1/2 [F-]
d) 2[NO3-]
17. Which of the following is a buffer?
a) NaOH + CH3COOH
b) NaOH + Na2SO4
c) K2SO4 + H2SO4
d) NH4OH + NaOH
18. For the following three reactions I, II and III, equilibrium constants are given
CO(g) + H2 O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + H2(g); K1
CH4(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + 3 H2(g); K2
CH4(g) + 2 H2O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + 4 H2(g); K3
Which of the following relations is correct?
a) K1 √(K2) = K3
b) K2 K3 = K1
c) K3 = K1 K2
d) K3 K23 = K12
19. 0.1 mole of N2 O4 (g) was sealed in a tube under one atmospheric conditions at 25℃. Calculate the number of moles of NO2 (g) present, if the equilibrium N2O4(g) ⇌ 2 NO2(g) (Kp=0.14) is reached after some time
a) 0.036
b) 36.00
c) 360.0
d) 3.600
20. A buffer solution is prepared by mixing 0.1 M ammonia and 1.0 M ammonium chloride. At 298 K, the pKb of NH4OH is 5.0.The pH of the buffer is
a) 10.0
b) 9.0
c) 6.0
d) 8.0
21. Which of the following molecules acts as a Lewis acid?
a) (CH3)3N
b) (CH3)3B
c) (CH3)2O
d) (CH3)3P
22. Which among the following is an electron deficient compound?
a) NF3
b) PF3
c) BF3
d) AsF3
23. Identify the correct order of acidic strength of CO2, CuO, CaO, H2O:
a) CaO < CuO < H2O < CO2
b) H2O < CuO < CaO < H2O
c) CaO < H2O < CuO < CO2
d) H2O < CO2 < CaO < CuO
24. Which of the following is a strong acid?
a) HClO4
b) HBrO4
c) HIO4
d) HNO3
25. According to Arrhenius concept the, strength of an acid depends on:
a) Hydrolysis
b) Concentration of acid
c) H+ ions furnished by acid
d) Number of mole of base used for neutralization
Answers
1. d 2. a 3. a 4. a 5. c 6. b 7. a 8. d 9. d 10. d 11. b 12. a 13. c 14. d 15. c 16. c 17. a 18. c 19. a 20. d 21. b 22. c 23. a 24. a 25. c
Solutions
1 (d)

The solution contains weak acid 0.5 Mol + its conjugate base 0.5 Mol and thus, acts as buffer.
2 (a)
Aqueous solution of 1M NaCl and 1M HCl is not a buffer but pH < 7.
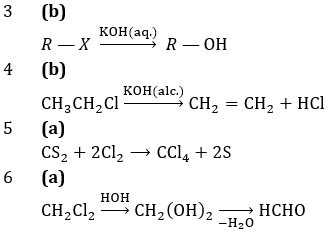
3 (a)
Reaction is exothermic and volume is decreasing from left to right, so for higher production of SO3, there should be low temperature and high pressure
4 (a)
The acid is called strong acid when it ionise up to great extent
i.e., if its Ka value is large.
We know that pKa=log (1/Ka)
5 (c)

6 (b)
H2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ 2 HCl(g)
We know that,
Kp = Kc.(RT)(∆ng)
∆ng = no. of moles of gaseous products – no. of moles of gaseous reactants
= 2-2=0
Kp = Kc.(RT)0
Kp = Kc
7 (a)
NaH2PO4 + H3PO4; NaH2PO4 + Na2HPO4; Na2HPO4 + Na3PO4.
9 (d)

solution will give highest concentration of [OH-]. Hence, it has highest pH.
10 (d)

Thus, solubility order= MX > M3X > MX2
11 (b)
Basic strength ∝ dissociation constant of base (Kb).
So, smaller the value of Kb weaker will be the base.
The weakest base will have smallest value of Kb.
∵ C6H5NH2(aniline) has smallest value of Kb .
∴ It is weakest base.
12 (a)
α= (number of mole dissociated)/(total mole present)
= 10-7/(1000/18)= 1.8×10-9= 1.8×10-7%
Total mole of H2O in 1 litre= 1000/18
13 (c)
A precipitate is formed when the ionic product exceeds the solubility product.
i.e., [A+][B-] > Ksp
14 (d)
2 HgNO3 + 2 HCl ⟶ Hg2Cl2 + 2 HNO3;
Hg2Cl2 in insoluble in water.
15 (c)
Lewis bases are electrons rich compounds.
(i) NH3 and H2O are Lewis bases because they have lone pair of electron.
(ii)AlCl3 is Lewis acid because it can accept electrons.
16 (c)
Ba(NO3)2 gives NO3-, Ba2+ ions, hence Ba2+ ion increases. To keep Ksp constant, [F-] decreases. Thus, it is represented as 1/2 [F-]
18 (c)
As equation ‘III’ is obtained on adding equation ‘I’ and equation ‘II’, so K3 = K1.K2.
19 (a)

Thus, [NO2 ]=2×0.018=0.036 mol
20 (d)
From Henderson equation

pH+pOH=14

pOH= 6
pH + pOH= 14
pH + 6= 14
pH= 14-6= 8
21 (b)
It has sextet of electron and can accept lone pair of electron.
22 (c)
BF3 is electron deficient compound because B has six electrons in outermost orbit. It has incomplete octet. So, it is an electron deficient molecule.
23 (a)
Metal oxides are basic, non-metal oxides are acidic. CaO is more basic than CuO. Water (H2O) is amphoteric.
24 (a)
The acidic character of oxy-acids decreases down the group and increases along the period. Also, higher ox.no. of non-metal in oxy-acid shows more acidic nature.
25 (c)
Follow Arrhenius concept.
Question 1-25
26. H2 + I2 ⇌ 2 HI
In the above equilibrium system, if the concentration of the reactants at 25℃ is increased, the value of K_c will
a) Increase
b) Decrease
c) Remains the same
d) Depends on the nature of the reactants
27. 0.04 g of pure NaOH is dissolved in 10 litre of distilled water. The pH of the solution is:
a) 9
b) 10
c) 11
d) 12
28. What is the equilibrium expression for the reaction, P4(s) + 5 O2(g) ⇌ P4O10(s)?
a) Kc = 1/[O2]5
b) Kc = [O2]5
c) Kc = ([P4O10]) / (5[P4][O2])
d) Kc = ([P4O10]) / ([P4][O2]5)
29. When 10-8 mole of HCl is dissolved in one litre of water, the pH of the solution will be:
a) 8
b) 7
c) Above 8
d) Below 7
30. A physician wishes to prepare a buffer solution at pH=3.58 that efficiently resists a change in pH yet contains only small conc. of the buffering agents. Which one of the following weak acid together with its sodium salt would be best to use?
a) m-chloro benzoic acid (pKa = 3.98)
b) p-chlorocinnamic acid (pKa = 4.41)
c) 2,5-dihydroxy benzoic acid (pKa = 2.97)
d) Acetoacetic acid (pKa = 3.58)
31. The pH of 10-8 M HCl solution is
a) 8
b) More than 8
c) Between 6 and 7
d) Slightly more than 7
32. A certain buffer solution contains equal concentration of X- and HX. The Ka for HX is 10. The pH of the buffer is:
a) 7
b) 8
c) 11
d) 14
33. 100 mL of 0.01 M solution of NaOH is diluted to 1 dm3. What is the pH of the diluted solution?
a) 12
b) 11
c) 2
d) 3
34. Which of the following salt does not get hydrolysed in water?
a) KClO4
b) NH4 Cl
c) CH3COONa
d) None of these
35. A higher value for equilibrium constant, K shows that:
a) The reaction has gone to near completion towards right
b) The reaction has not yet started
c) The reaction has gone to near completion towards left
d) None of the above
36. Which one is least basic?
a) CH3NH2
b) NH3
c) C2H5NH2
d) C6H5NH2
37. The aqueous solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate is:
a) Acidic
b) Neutral
c) Basic
d) None of these
38. 3.2 moles of hydrogen iodide were heated in a sealed bulb at 444℃ till the equilibrium state was reached. Its degree of dissociation at this temperature was found to be 22%. The number of moles of hydrogen iodide present at equilibrium are
a) 1.876
b) 2.496
c) 3.235
d) 4.126
39. In the reactions, PCl5 ⇌ PCl3 + Cl2, the amounts of PCl5, PCl3 and Cl2 at equilibrium are 2 mole each and the total pressure is 3 am. The equilibrium constant Kp is:
a) 1.0 atm
b) 2.0 atm
c) 3.0 atm
d) 6.0 atm
40. Which of the following is correct for the reaction?
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g)
a) Kp = Kc
b) Kp&It;kc
c) Kp>Kc
d) Pressure is required to predict the correlation
41. The graph relates ln Keq vs 1/T for a reaction. The reaction must be:

a) Exothermic
b) Endothermic
c) ∆H is negligible
d) Highly spontaneous at ordinary temperature
42. 0.1 millimole of CdSO4 are present in 10 mL acid solution of 0.08 N HCl. Now H2S is passed to precipitate all the Cd2+ ions. The pH of the solution after filtering off precipitate, boiling of H2S and making the solution 100 mL by adding H2 O is:
a) 2
b) 4
c) 6
d) 8
43. Calculate the pH of a solution in which hydrogen ion concentration is 0.005 g-equi/L?
a) 2.3
b) 2.8
c) 2.9
d) 2.6
44. In 1L saturated solution of AgCl [Ksp (AgCl)1.6 10^10], 0.1 mole of CuCl [Ksp (CuCl) 1.0 106] is added. The resultant concentration of Ag in the solution is 1.6 10x. The value of 'x' is
a) 3
b) 5
c) 7
d) 9
45. Eight mole of a gas AB3 attain equilibrium in a closed container of volume 1 dm3 as, 2 AB3 ⇌ A2 (g) + 3 B2(g). If at equilibrium 2 mole of A2 are present then, equilibrium constant is :
a) 72 mol2 L-2
b) 36 mol2 L-2
c) 3 mol2 L-2
d) 27 mol2 L-2
46. Which of the following is most soluble in water?
a) MnS (Ksp=8 × 10-37)
b) ZnS (Ksp=7 × 10-16)
c) Bi2S3 (Ksp=1 × 10-70)
d) Ag2S (Ksp=6 × 10-51)
47. At a given temperature the Kc for the reaction, PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) is 2.4 ×10-3. At the same temperature, the Kc for the reaction
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ PCl5(g) is:
a) 2.4 ×10-3
b) -2.4 × 10-3
c) 4.2 ×10-2
d) 4.8 ×10-2
48. If the solubility of lithium sodium hexafluoroaluminate, Li3Na3 (AlF6)2 is 'a^' mol/litre, its solubility product is equal to:
a) a2
b) 12a2
c) 18a3
d) 2916a^8
49. Approximate relationship between dissociation constant of water (K) and ionic product of water (Kw) is
a) Kw = K
b) Kw = 55.6 × K
c) Kw = 18 × K
d) Kw = 14 × K
50. Degree of dissociation of 0.1 N CH3COOH is (dissociation constant =1×10-5)
a) 10-5
b) 10-4
c) 10-3
d) 10-2
Answers
26. c 27. b 28. a 29. d 30. d 31. c 32. b 33. b 34. a 35. a 36. d 37. c 38. b 39. a 40. b 41. a 42. a 43. a 44. c 45. d 46. b 47. c 48. d 49. b 50. d
Solutions
We hope our website has been helpful in your preparation. Thanks for visiting.





























 C2H5X, the order of reactivity is:
C2H5X, the order of reactivity is: