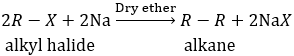Haloalkanes & Haloarenes MCQ Questions for NEET
Hello NEET aspirants. In this article we brought to you the MCQ questions from class 12 chapter named as "Haloalkanes and Haloarenes". Answer key and detailed solutions are also provided in this article so that you don't have any doubts left for any of the questions. Good Luck!
For chapter-wise MCQ questions, visit the following links:
Questions
1. Among the following the one that gives positive iodoform test upon reaction with I2 and NaOH is
a) CH3CH2CH(OH)CH2CH3
b) C6H5CH2CH2OH
c) H3C-CH(CH3)-CH2OH
d) PhCHOHCH3
2. Vicinal and geminal dihalides can be distinguished by:
a) KOH (aq.)
b) KOH (alc.)
c) Zn dust
d) None of these
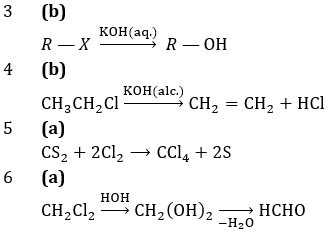
3. An alkyl halide may be converted into an alcohol by:
a) Addition
b) Substitution
c) Dehydrohalogenation
d) Elimination
4. Dehydrohalogenation in haloalkanes produces:
a) A single bond
b) A double bond
c) A triple bond
d) Fragmentation
5. Chlorination of CS2 gives:
a) CCl4
b) CS2Cl2
c) CH4
d) CHCl3
6. Methylene chloride on hydrolysis yields:
a) HCHO
b) CH3CHO
c) CHCl3
d) CH3COCl
7. The greater the ionic character of the carbon metal bond:
a) The more reactive is the organometallic compound
b) The less reactive is the organometallic compound
c) Both are correct
d) None of the above is correct
8. For the reaction,
C2H5OH + HX  C2H5X, the order of reactivity is:
C2H5X, the order of reactivity is:
a) HI > HCl > HBr
b) HI > HBr > HCl
c) HCl > HBr > HI
d) HBr > HI > HCl
9. The order of reactivities of methyl halides in the formation of Grignard reagent is
a) CH3I > CH3Br > CH3Cl
b) CH3Cl > CH3Br > CH3I
c) CH3Br > CH3Cl > CH3I
d) CH3Br > CH3I > CH3Cl
10. The antiseptic character of iodoform is due to:
a) Its poisonous nature
b) Unpleasant smell
c) Liberation of free iodine
d) None of the above
11. On treating a mixture of two alkyl halides with sodium metal in dry ether, 2-methyl propane was obtained. The alkyl halides are
a) 2-chloropropane and chloromethane
b) 2-chloropropane and chloroethane
c) Chloromethane and chloroethane
d) Chloromethane and 1-chloropropane
12. The IUPAC name of the compound, (CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br is:
a) 2-methyl-3-bromopropane
b) 1-bromopentane
c) 2-methyl-4-bromobutane
d) 1-bromo-3-methylbutane
13. The given reaction is an example of,
C2H5Br + KCN(aq.) ⟶ C2H5CN + KBr
a) Elimination
b) Nucleophilic substitution
c) Electrophilic substitution
d) Redox change
14. Which one of the following compound reacts with chlorobenzene to produce DDT?
a) Acetaldehyde
b) Nitrobenzene
c) m-chloroacetaldehyde
d) Trichloroacetaldehyde
15. Preparation of alkyl halides in laboratory is least preferred by:
a) Halide exchange
b) Direct halogenation of alkanes
c) Treatment of alcohols
d) Addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes
16. Which one of the following pairs is the strongest pesticide?
a) Chloroform and benzene hexachloride
b) DDT and 666
c) 666 and ether
d) isocyanides and alcohol
17. Iodoform gives a precipitate with AgNO3 on heating but chloroform does not because:
a) Iodoform is ionic
b) Chloroform is covalent
c) C—I bond in iodoform is weak and C—Cl bond in chloroform is strong
d) None of the above
18. Which reagent is useful in increasing the carbon chain of an alkyl halide?
a) HCN
b) KCN
c) NH4CN
d) AgCN
19. Chloroform on reaction with conc. HNO3 gives an insecticide and war gas known as:
a) Chloropicrin
b) Nitromethane
c) Picric acid
d) Acetylene
20. Aryl halides are less reactive towards electrophiles than alkyl halides due to:
a) Resonance
b) Stability of carbonium ions
c) High boiling point
d) None of the above
21. Carbon tetrachloride reacts with steam at 500℃ to give:
a) COCl2
b) CHCl3
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
22. Chloroform on reaction with acetone yields:
a) Insecticide
b) Hypnotic agent
c) Analgesic
d) Isocyanide
23. In Wurtz reaction alkyl halide reacts with
a) Sodium in ether
b) Sodium in dry ether
c) Sodium only
d) Alkyl halide in ether
24. When iodoform is heated with silver powder it forms:
a) Acetylene
b) Ethylene
c) Methane
d) Ethane
25. 1,3-dibromopropane reacts with metallic zinc to form:
a) Propene
b) Cyclopropane
c) Propane
d) Hexane
Answers
| 1. d | 2. a | 3. b | 4. b | 5. a |
| 6. a | 7. a | 8. b | 9. a | 10. c |
| 11. a | 12. d | 13. b | 14. d | 15. b |
| 16. b | 17. c | 18. b | 19. a | 20. a |
| 21. a | 22. b | 23. b | 24. a | 25. b |
Explanation
1 (d)
For positive iodoform test, alcohol molecule must have
2 (a)
8 (b)
HI reacts with C2H5OH even in absence of ZnX2. Larger is bond length, more is reactivity.
9 (a)
Among alkyl halides, iodides are least stable, hence these form Grignard reagent easily. Hence, the correct order of reactivity in formation of Grignard reagent is
CH3I > CH3Br > CH3Cl
10 (c)
The I2 has antiseptic nature.
11 (a)
This is Wurtz reaction. 2-chloropropane and chloromethane reacts in presence of dry ether t form 2-methyl propane.
13 (b)
Br is replaced by a nucleophileCN-.
15 (b)
A mixture of halides is formed.
16 (b)
DDT and 666 (C6H6Cl6 or benzene hexachloride) is the pair of strongest pesticides.
17 (c)
Thus, decomposition of CHI3 occurs.
18 (b)
CH3X + KCN ⟶ CH3CN
19 (a)
CHCl3 + HNO3 ⟶ CCl3∙NO2 + H2O∙CCl3∙NO2 is called chloropicrin.
20 (a)
Aryl halides show resonance in their structure.
21 (a)
CCl4 + H2O(v) ⟶ COCl2 + 2 HCl
23 (b)
In Wurtz reaction alkyl halide react with sodium in dry ether to produce alkane having double number of carbon atoms as in alkyl halide.
24 (a)
CH3I + 6 Ag + I3HC ⟶ C2H2 + 6 AgX
If you want more questions on this chapter, you can ask in the comment section. We hope this article has been helpful. Thaks for visiting our website.