Chemical Coordination MCQ Questions for NEET
Hello NEET aspirants. In this article, we will be sharing multiple choice questions from chapter Chemical Coordination. We have also shared answer keys and detailed solutions so that you can clear your doubts. We assure you that this article will be a great help in your preparations.
For chapter-wise MCQ questions, visit the following links:
Question 1-20
1. Androgens regulates
a) Development of accessory sex organs
b) Muscular growth
c) Maturation of accessory sex organs
d) All of the above
2. Progesterone hormone is secreted by
a) Corpus albicans
b) Corpus callosum
c) Corpus luteum in ovaries
d) Corpus uteri
3. Injury to adrenal cortex is not likely to affect the secretion of which one of the following?
a) Aldosterone
b) Both androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone
c) Adrenaline
d) Cortisol
4. Hormones are non-nutrient chemicals, which acts as…….. messengers and are produced in trace amount
a) Intercellular
b) Intracellular
c) Extracellular
d) None of these
5. Insulin receptors are
a) Extrinsic protein
b) Intrinsic protein
c) G – protein
d) Trimeric protein
6. Choose the correct option for A to D
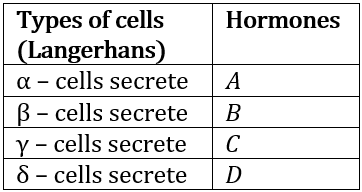
b) A-Insulin, B-Glucagon, C-Gastrin, D-Somatostatin
c) A-Insulin, B-Glucagon, C-Somatostatin, D-Gastrin
d) A-Glucagon, B-Insulin, C-Somatostatin, D-Gastrin
7. ‘GIP’ stimulates the release of
a) Glucagon
b) Insulin
c) Calcitonin
d) Thyrocalcitonin
8. The thyroid gland is composed of …A… lobes which are located on either side of the …B… the lobes are interconnected with a thin flap of connective tissue called …C…
Select the correct combination for A, B and C
a) A-3, B-trachea, C-isthmus
b) A-4, B-trachea, C-isthmus
c) A-2, B-trachea, C-isthmus
d) A-1, B-trachea, C-isthmus
9. Some hormone need the secondary messenger, because
a) They need activator
b) They can’t cross cells membrane
c) They can cross cells membrane
d) They need a prosthetic group
10. Sex hormones can work without the help of
a) Insulin
b) Placenta
c) Pituitary
d) gonadotropins
11. Estrogen
a) Stimulate the growth of ovarian follicle
b) Stimulate the appearance of secondary sex characters
c) Stimulate the growth of mammary gland
d) All of the above
12. In human adults females, oxytocin
a) Is secreted by anterior pituitary
b) Stimulates growth of mammary glands
c) Stimulate pituitary to secrete vasopressin
d) Causes strong uterine contractions during parturition
13. The hormone that increases the blood calcium level and decreases its excretion by kidney is
a) Parathormone
b) Calcitonin
c) Thyroxine
d) Insulin
14. Gastrointestinal hormones are
a) Steroidal in nature
b) Proteinaceous in nature
c) Glycoproteinaceous in nature
d) Both (a) and (b)
15. I. Glucagon
II. Epinephrine
III. Steroid hormone
IV. Idothyronine
Among the given hormones which needs secondary messenger
a) I and III
b) III and IV
c) I and II
d) IV and I
16. A steroid hormone which regulates glucose metabolism is
a) Cortisol
b) Corticosterone
c) 11- deoxycorticosterone
d) Cortisone
17. The activity of formation of milk is regulated by the activity of …A… . While the ejection of milk is controlled by …B… hormone
Here, A and B refers to
a) A-oxytocin; B-prolactin
b) A-prolactin; A-oxytocin
c) A-prolactin; B-prolactin
d) A-oxytocin; B-prolactin
18. Feeling the tremors of an earthquake, a scared resident of seventh floor of a multistoreyed building starts climbing down the stairs rapidly. Which hormone initiates this action?
a) Thyroxine
b) Adrenaline
c) Glucagon
d) Gastrin
19. Endocrine glands are
a) Ductless glands whose secretions pour directly into blood
b) Have ducts and pour their secretions into blood directly
c) Have ducts which straightway pour secretions into target organs
d) All of the above
20. Pheromones are also called
I. ectohormones
II. sex attractants
III. semichemicals
The correct option is
a) I and III
b) I and III
c) I, II and III
d) II and III
Answer
Solution
1 (d)
Androgen regulate the development, maturation and functions of the male accessory sex organs like epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, etc. These hormones stimulate muscular growth, growth of facial and axillary hair, aggressiveness, low pitch of voice, etc. Androgens play a major stimulatory role in process of spermatogenesis (formation of spermatozoa)
2 (c)
Secretion of progesterone from corpus luteum, is stimulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) of anterior pituitary.
3 (c)
Adrenaline (epinephrine) and noredrenaline (norepinephrine) are catecholamines hormones which are secreted from adrenal medulla part of adrenal gland. As adrenal gland is divided into-adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla. These hormones are protienaceous in nature and derived from amino acids tyrosine. Thus, injury to adrenal cortex will not affect the secretion of adrenaline.
4 (a)
Hormones are non-nutrient chemicals which act ass intercellular messengers and are produced in trace amounts
5 (a)
Insulin receptors are extrinsic proteins these are complex of two α and two β- subunits held together by disulphide bond.
6 (a)
Pancreas is the Second Largest Endocrine Gland

7 (b)
GIP (Gastro Inhibitory Polypeptide) inhibits gastric acid secretion and stimulates insulin release
8 (c)
A-2, B-trachea, C-isthmus
9 (b)
The hormones which are proteinaceous in nature generally can’t pass through the cell membrane. So, they generate the secondary messenger like (Ca^(2+), IP_3) which regulate the further changes in target cell
10 (a)
Insulin hormone regulates carbohydrate metabolism. Sexual reproductive system does not apparently involve it.
11 (d)
Estrogen produces wide ranging actions such as stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs, development of growing ovarian follicle, appearance of female secondary sex characters (e.g., high pitch voice, etc.), mammary glands development. Estrogen also regulate the female sexual behaviour
12 (b)
Oxytocin stimulates growth of mammary glands in human adult.
13 (a)
Parathormone secreted by parathyroid gland regulates the calcium and phosphate balance between the blood and the other tissues. It increases the plasma Ca^(2+)represses plasma phosphate and decreases Ca^(2+) excretion by the kidney.
14 (b)
There are bunch of hormones, neuropeptides and neurotransmitters that affect gastrointestinal function. The GI (gastrointestinal) endocrine system diffuses and its endocrine cells are distributed differentially in the mucosal epithelium along the length of digestive tract. Gastrointestinal hormones are proteinaceous in nature
15 (c)
Glucagon and epinephrine hormone are protein in nature. They produces the secondary messenger for their action
16 (a)
Cortisol or hydrocortisone is the principal glucocorticoid hormone of many mammals including humans. It is secreted from zonafasiculata layer of adrenal cortex. It regulates the glucose metabolism and promotes gluconeogenesis, especially during starvation and raises blood pressure.
17 (b)
A-Prolactin, B-Oxytocin
19 (a)
Endocrine glands (ductless glands) or gland of internal secretion have no ducts and their secretion get absorbed into the immediate surrounding blood circulation to reach the specific organ to initiate a particular metabolic change.
20 (c)
Pheromone are chemicals used for communication amongst individual of same species. Also known as ectohormones/sex attractants/semi chemicals. Pheromones involve a specific response in other members like recognition, warning and attraction
Question 21-40
21. Sertoli cells are regulated by the pituitary hormone known as
a) FSH
b) GH
c) Prolactin
d) LH
22. Which of the following is gastrointestine hormone?
a) Prolactin
b) Enterogastrone
c) GH
d) FSH
23. Islets of Langerhans is a normal human pancreas comprise only
a) 2-3% of pancreatic tissue
b) 1-2% of pancreatic tissue
c) 3-4% of pancreatic tissue
d) 4-5% of pancreatic tissue
24. Which is the function of norepinephrine?
a) Increase blood pressure
b) Urine formation
c) Increase secretion of adrenaline
d) None of the above
25. Correct order of action of hydrophilic hormones
I. Hormones bind to plasma membrane
II. Physiological response
III. Biochemical response
IV. Generation of secondary messenger
Choose the correct option
a) I, II, III, IV
b) II, I, III, IV
c) I, IV, III, II
d) III, I, II, IV
26. To yield more milk, cow is injected with
a) Sorbitol
b) Prolactin
c) Gonadotrophs
d) Sterol
27. FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) is produced by
a) Adrenal cortex
b) Anterior pituitary lobe
c) Middle pituitary lobe
d) Posterior pituitary lobe
28. Calcium level decreases in the blood due to hyposecretion of
a) Parathyroid hormone
b) Calcitonin
c) Thyroxine
d) Adrenaline
29. I. Somatostatin inhibits intestinal absorption of glucose
II. Leydig’s cell secrete progesterone
III. Melatonin is secreted by pineal gland
IV. Myxoedema is a thyroid disorder
V. Neurohypophysis secreted ACTH
Select the correct statements and choose the option
a) I, III and IV
b) II, III and V
c) I, IV and V
d) II, IV and V
30. Hypothyroidism causes
a) Myxoedema
b) Cretinism
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Exophthalmicgoitre
31. Which one of the following is not an endocrine gland?
a) Kidney
b) Thyroid
c) Adrenal
d) Pituitary
32. Pituitary gland is derived from
a) Ectoderm
b) Endoderm
c) Mesoderm
d) None of these
33. ‘ANF’ is secretes by
a) Venous wall of heart
b) Atrial wall of heart
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of these
34. Tyrosine is the precursor of
a) Adrenaline
b) Noradrenaline
c) Testosterone
d) Both (a) and (b)
35. Which one of the following four glands is correctly matched with the accompanying description?

36. Generally the steroid hormones are derived from
a) Proteins
b) Carbohydrates
c) Cholesterol
d) Glycoprotein
37. Which hormone causes dilation of blood vessels, increased oxygen consumption and glycogenolysis?
a) ACTH
b) Insulin
c) Adrenaline
d) Glucagon
38. In Cushing’s syndrome, there is
a) An increase in blood glucose level
b) Hypertrophy of the skeletal muscles
c) A fall in plasma cortisol
d) A thickening of the skin
39. Progesterone is secreted by
a) Corpus luteum
b) Uterus
c) Placenta
d) Graafian follicle
40. Thymus gland releases _____ hormone
a) T4
b) T3
c) Thymosins
d) TCT
Answer
Solution
Detailed solutions of questions 21-40 are given below:
21 (a)
Sertoli cells are the cells that line the seminiferous tubules in the testis. These cells protect the spermatids and convey nutrients to both the developing and mature spermatozoa. Sertoli cells are regulated by FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) as the FSH receptors are confined to the sertoli cells.
22 (b)
Enterogastrone hormone produced by small intestine slows down secretion of gastric juice. Enterokinase is an enzyme in intestinal juice that activates trypsinogen to trypsin.
23 (b)
1 to 2% pancreatic tissue
24 (a)
Norepinephrinc is secreted from adrenal medulla. It rises blood pressure.
25 (c)
General steps in hydrophilic or water soluble or protein nature hormone action
26 (b)
Prolactin is a lactogenic hormone produced by anterior lobe of pituitary gland. It stimulates milk production in cow.
27 (b)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) is produced from anterior pituitary lobe
28 (a)
Parathormone is secreted from parathyroid gland. This hormone helps to regulate the metabolism of calcium and certain other minerals like phosphate. Combined effect of parathormone and calcitonin normally maintain the blood calcium level.
29 (a)
(i) Leydig cells secretes testosterone hormone which enhances the spermatogenesis
(ii) Neurohypophysis secretes oxytocin and ADH. ACTH is provide cell mediated immunity secreted by adenohypophysis
30 (c)
Hypothyroidism causes both cretinism and myxoedema.
31 (a)
Thyroid gland, adrenal gland and pituitary gland are endocrine glands but kidney is an excretory organ.
32 (a)
Pituitary gland, pineal gland, mammary glands and medulla of adrenal gland are derived from ectoderm.
33 (b)
The atrial wall of our heart secretes very important peptide hormone called Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF), which is peptide in nature. ANF decreases blood pressure. When blood pressure is increased, ANF is secreted which causes dilation of the blood vessels. This reduces the blood pressure
34 (d)
The conversion of tyrosine to epinephrine involves four steps:
(i) Ring hydroxylation
(ii) Decarboxylation
(iii) Side chain hydroxylation
(iv) N-methylation

35 (b)
Thymus is an endocrine gland, which is active in young ones but gradually becomes inconspicuous after sexual maturity. Like other lymphoid tissues, thymus undergoes atrophy in response to adrenoglucocorticoids.
36 (c)
Sterol (cyclopenta noperhydro phenanthrine ring) generally gives rise to most of the steroid hormones

37 (c)
Adrenaline (epinephrine) is a hormone produced by adrenal medulla and is secreted in great amounts during emotional stress. It elevates the glucose level in blood stream (by glycogenolysis) which is accompanied by increase inoxygen consumption, body temperature, heat production. Adrenaline also cause an increase in the flow of blood by dilating blood vessels.
38 (a)
Cushing’s syndrome is the result of excessive secretion of cortisol by adrenal cortex. This leads to increased protein breakdown which is manifest by wasting of the skeletal muscle and a decreased skin thickness (which thus bruises easily). High level of cortisol in blood may also elevate the blood glucose level.
39 (a)
Progesterone is a principal female sex hormone. It is steroid and secreted during the latter half of the menstrual cycle in human females by temporary endocrine tissue, the corpus luteum.
40 (c)
Thymus gland secretes the peptide hormones called thymosins. Thymosin plays a major role in the differentiation of T-lymphocytes, which provides cell-mediated immunity. In addition, thymosins also promote the production of antibodies to provide humoral immunity.
These were the 40 questions from chemical coordination chapter. Our website also provide chapter wise mcq questions for various exams such as NEET. You can also visit various chapters included in Biology, Chemistry and Physics for your NEET preparations. Thanks for visiting our website.
