Hello NEET exam aspirants. In this article, we will post MCQs from class 11 biology chapter "Transport in plants". If you are preparing for upcoming NEET exam, these questions can be your ultimate source of revision. You can also match your answers and see detailed solutions as well to clear your doubts.
For chapter-wise MCQ questions, visit the following links:
Transport in Plants NEET MCQ Questions
Question 1-25
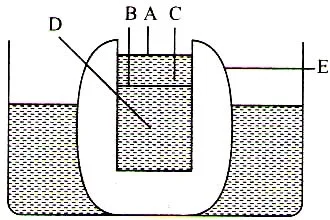
1. The given diagram shows cotransport method of two molecule. Labelled it correctly and choose the correct option accordingly

a) A-Uniport, B-Symport, C-Antiport
b) A-Uniport, B-Antiport, C-Symport
c) A-Symport, B-Uniport, C-Antiport
d) A-Antiport, B-Uniport, C-Uniport
2. What are the aquaporins in facilitated diffusion process?
a) Membrane proteins
b) Carrier proteins
c) Channel proteins
d) Carrier lipids
3. Which of the following osmotic situations does the figure demonstrate?

a) Plasmolysis
b) Turgid
c) Reverse plasmolysis
d) Diffused
4. Read the following statement and choose the correct one from the codes given below
I. The apoplastic movement of water takes place exclusively through intercellular spaces and cell wall without crossing any membrane
II. Symplastic movement occurs from cell to cell through plasmodesmata, i.e., adjacent cells are connected through plasmodesmata
III. Permeability of a membrane depends on its composition and chemical nature of the solute
IV. Solutes present in a cell increases the free energy of the water or water potential
a) I, II and III
b) I, II and IV
c) II and IV
d) I and IV
5. When sugars enter sieve tubes, water flows by osmosis, resulting in
a) Water potential
b) Osmotic gradient
c) Turgor pressure
d) DPD
6. The evaporative loss of water from the exposed part of plant is called
a) Transpiration
b) Guttation
c) Loss of water
d) Water bleeding
7. Which one of the following is not related to guttation?
a) Water is given out in the form of droplets
b) Water given out is impure
c) Water is given out during daytime
d) Guttation is of universal occurance
8. Whose water potential is less than water potential of root hair during the water absorption by root hair?
a) Gravitational water
b) Soil solution
c) Pure water
d) Vacuolar sap
9. A thin film of water is held by the soil particles under the influence of internal attractive force. It is called
a) Hygroscopic water
b) Gravitational water
c) Combined water
d) Capillary water
10. Study the following statement and choose the correct option(s) from the codes from below
I. Root pressure provides a light push in the overall process of water transport
II. Root pressure causes the flow of water faster through xylem than it can be lost by transportation
III. In symplast pathway, water move exclusively through the cell wall and intercellular spaces
IV. Guttation is a cause of transpiration pull
V. Most plants fulfill their water requirement by transpiration pull
a) I, II and III are correct while IV and V are incorrect
b) IV and V are correct while I, II and III are incorrect
c) I and V are correct
d) II and III are correct while I, IV and IV are incorrect
11. What is required for the transport of substances through a membrane from a region of lower concentration to higher concentration?
a) Input of energy
b) Output of energy
c) Facilitated diffusion
d) Nothing is required
12. Which of the following statement is correct?
a) DPD=OP-WP
b) DPD=OP+WP
c) DPD=WP-OP
d) DPD=TP+OP
13. Choose the correct combination of labeling of stomatal apparatus of dicot and monocot leaves

a) A-Epidermal cells B-Subsidiary cells C-Chloroplast D-Guard cells E-Stomatal aperature
b) A-Epidermal cells B-Guard cells C-Chloroplast D-Subsidiary cells E-Ctomatal aperature
c) A-Epidermal cells B-Subsidiary cells C-Chloroplast D- Stomatal aperature E- Guard cells
d) A- Subsidiary cells B- Epidermal cells C-Chloroplast D- Stomatal aperature E- Guard cells
14. In a plant organ, which is covered by periderm and in which the stomata are absent, some gaseous exchange still takes place through
a) Aerenchyma
b) Trichomes
c) Pnenumatophores
d) Lenticels
15. Identify the correct statements from the following:
I.Accumulation of K^+ ions in the guard cells does not require energy.
II.A high pH favours stomatal opening.
III.Movement of chloride ions into the guard cells accrues in the response to the electrical differential created by K^+ ions.
IV.With the entry of several K^+ ions and chloride ions, the water potential of guard cells increases.
a) I and III
b) I and II
c) II and III
d) III and IV
16. Which one of the following is the reason for higher rate of transpiration in Sorghum as compared to maize?
a) Increased shoot/root ratio
b) Increased rate of respiratory quotient
c) Increased rate of phototsynthesis
d) Decreased shoot/root ratio
17. If turgidity of a cell surrounded by water increases, the wall pressure will
a) Increase
b) Decrease
c) Fluctuate
d) Remain unchanged
18. In plants; which of the following are/is translocated through phloem?
a) Hormones
b) Amino acids
c) Sugars
d) All of these
19. Root pressure is due to
a) Diffusion
b) Passive transport
c) Active transport
d) Osmosis
20. What is depicted by the given diagram below?

a) Measuring the rate of transpiration
b) Demonstration of ascent of sap
c) Demonstration of transpiration
d) Both (a) and (c)
21. Choose correct statements regarding the flow of sap in xylem?
I. Flow is driven by higher concentration of sugar in the vessel elements
II. Flow from root to twigs and leaves would be reduced if leaves are removed
III. In the morning, sap begins to flow first in the twig then in trunk
IV. Rapid flow of water put tissues under pressure much more than atmospheric pressure
a) I and IV
b) II and III
c) I, II, III and IV
d) No one is correct
22. Stomatal opening is regulated by
a) Light
b) Temperature
c) Atmospheric humidity
d) Wind
23. The direction of movement in phloem is …A… and that of xylem is …B… .
Choose the correct pair of options
a) A-downwards; B-downwards
b) A-only upwards; B-only downward
c) A-unidirectional; B-bidirectional
d) A-bidirectional; B-unidirectional
24. Which of the following theories for ascent of sap was proposed by an eminent Indian scientist J C Bose?
a) Pulsation theory
b) Relay pump theory
c) Transpiration pull theory
d) Root pressure theory
25. The potential energy of water is referred as
a) Water potential
b) Osmotic potential
c) Gravity potential
d) Pressure potential
Answers
Solutions
1 (b)
The given diagram represents the transport of two type of molecules by carrier proteins, which is achieved with the activity of membrane proton pump to solute exchange. ‘A’ depicts, uniport method of transport-molecule move across the membrane.
‘B’ shows antiport method and symport method (transport in same direction) is shown by ‘C’ in the given diagram.
2 (c)
Aquaporins are present in cell membranes. They facilitate the transport of water soluble substances through it. Aquaporins are also known as channel proteins.
3 (a)
Plasmolysis.
4 (a)
Addition of solutes in a system or cell decreases the energy of water. Pure water has the maximum diffusion pressure. Water potential or chemical potential of pure water is the difference in the free energy per unit molal volume of water in a system in reference to pure water at normal temperature and pressure.
5 (c)
The movement of sugars in the phloem begins at the source, where sugars are loaded (actively transported) into a sieve tube. Loading of the phloem steps up a water potential gradient that facilitates the mass movement in the phloem.
6 (a)
The evaporative loss of water in the form of vapours form the exposed part of plant is known as transpiration. This evaporative loss of water due to process of transpiration varies from plant, i.e., around 2 L per day in sunflower, while it is one tonne per day in elm tree. Rate of transpiration is affected by relative humidity, temperature, light, wind speed, atmospheric pressure and availability of water.
7 (c)
In herbaceous plants, when root pressure is high and transpiration is low, plants may lose this extra water in liquid drops from margins of leaves. This process is called guttation. It is very common during warm and humid nights. These water drops contain salts, amino acids, etc.
8 (d)
Water always moves from area of high water potential to area of low water potential, i.e., from less negative to more negative. During water absorption by root hair, the water movement is possible if water potential of vacuolar sap is lower than root hair.
9 (a)
The water remaining in dry soil and held as very thin films around the soil particles is called hygroscopic water.
10 (c)
Root pressure, a manifestation of active water absorption is developed in xylem sap of roots of same plants. It maintains optimum metabolic activity and reduce transpiration and provide a light push in overall process of water transport because root pressure cannot transport water upto the whole length of plant. Movement of water is shown through xylem.
In symplastic movements, movement of water occurs from cell to cell through their protoplasm, which are connected by a bridge called plasmodesmata
11 (a)
Transport of substances through membrane from region of higher concentration to lower concentration needs energy and transport is called active transport
12 (a)
The value by which the diffusion pressure of a solution is lower than that of pure solvent is known as diffusion pressure deficit.
DPD or SP=OP-TP
At the equilibrium TP=WP
DPD=OP-WP.
13 (a)
The stomatal aperture is surrounded by guard cells having chloroplasts
14 (d)
Mature stems of woody plants have a peripheral water proof tissue called cork (phellem). A number of scars known as lenticels are found on the surface of cork. Lenticels allow the gaseous exchange between atmosphere and living cells below the cork and also take parts in transpiration (0.1 %).
15 (c)
In the light, the pH of guard cells becomes increased due to consumption of CO_2 in the process of photosynthesis. Guard cells receive K^+ions from subsidiary cells. This decreases the water potential of guard cells and leads to migration of water from subsidiary cells to guard cells.
Uptake of K^+ ions is also balanced by Cl^- ions.
16 (a)
Sorghum has high shoot root ratio (due to more length) than maize. According to Parker (1949), the ratio of transpiration is directly proportional to shoot-root ratio.
17 (a)
If a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution/pure water, water starts moving in by endosmosis. As the volume of the protoplast increases, it begins to exert pressure against the cell wall (turgor pressure). Normally, wall pressure is equal and opposite to turgor pressure except when cell becomes flaccid, So if cell’s turgidity increases, wall pressure also increases.
18 (d)
Hormones, amino acids and sugars are transported or translocated through phloem
19 (d)
Stocking has defined root pressure as a pressure developed in the treachery elements of xylem as a result of metabolic activities of root. It is said to be a active process and appears due to osmosis.
20 (c)
It is demonstration of transpiration by bell jar experiment. It this experiment a potted plant is placed on a slab and a dry bell jar is inverted over it. Having sealed the edge of jar with wax or Vaseline, the whole apparatus is left undisturbed. After sometimes the inner surface of bell jar became misty due to transpiration by plant
21 (b)
Xylem sap is composed of minerals and water and is not driven by higher concentration of sugars, while rapid flow of water does not affect the conducting tissue and only the rate of transpiration is increased
22 (a)
The most significant physiological feature of stomata is their response to light. Generally stomata open in the day time, i.e., light and close at night or in darkness. These are called as photoactive stomata. However, in succulent plants like Kalanchoe of family- Crassulaceae, the stomata open at night and close in the day time. Such stomata are called scotoactive stomata.
23 (d)
The direction of movement in phloem is bidirectional and that of xylem is unidirectional. Since the source-sink relationship is variable, the direction of movement in the phloem can be upwards or downwards, i.e., bidirectional. This contrast with that of the xylem, where the movement is always unidirectional, i.e., upwards
24 (a)
Pulsation theory for ascent of sap was proposed by an eminent Indian scientist J C Bose.
25 (a)
The water potential is the chemical potential of water in a system or part of a system expressed in units of pressure and chemical potential of pure water at same atmospheric pressure and temperature.
Question 26-50
26. If two solutions have the same osmoregularity, they are said to be
a) Hypertonic
b) Hypotonic
c) Isotonic
d) None of these
27. Plant obtain carbon and most of their oxygen from
a) Soil
b) Water
c) CO_2 from the atmosphere
d) Symbiotic organisation
28. When plant cell is kept in saline drip, cell
a) Decrease in size
b) Bursts out
c) Increase in size
d) Unchanged
29. Carrier protein, which allows the diffusion of two type of molecules in the same direction is
a) Symport
b) Antiport
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) Uniport
30. Hydroponics is the method of
a) Water conservation
b) Plant development in water without soil
c) Plant development without soil
d) Plant development in saline soil
31. Imbibition is always accompanied by swelling or increase in the volume of imbibint However, the increase in the volume of the imbibant is
a) More than the volume of water imbibed
b) Same as the volume of the water imbibed
c) Less than the volume of the water imbibed
d) Depends upon the type of imbibant
32. Which of the following is responsible for the transport of water and minerals from roots to stems, leaves, flowers and fruits in rooted plants?
a) Xylem
b) Phloem
c) Either (a) or (b)
d) Both (a) and (b)
33. Loss of liquid water by guttation occurs through
a) Hydathodes
b) Stomata
c) Cuticle
d) Bark
34. The process by which water is absorbed by solids like colloid causing them to increase in volume, is called
a) Osmosis
b) Plasmolysis
c) Imbibition
d) Diffusion
35. Choose the correct combination of labeling of the potato osmoscope experiement.

36. How will you distinguish between the method of transport between xylem and phloem?
a) Active transport move xylem but not phloem sap
b) Transport, in xylem is unidirectional and saps move upward, while phloem sap moves ups and down
c) Transpiration does not move xylem sap, but it moves phloem saps
d) Transport of substances take place from source to sink by both the tissues
37. Which one of the following is not an antitranspirant?
a) PMA
b) BAP
c) Silicon oil
d) Low viscosity
38. Statoliths are involved in
a) Phototropism
b) Hydrotropism
c) Chemotropism
d) Gravitropism
39. In plasmolysed cell, the space between nucleus and plasma membrane is occupied by
a) Hypotonic solution
b) Hypertonic solution
c) Isotonic solution
d) Air
40. The sugarcane plant has
a) Dumb bell-shaped guard cells
b) Pentamerous flowers
c) Reticulate venation
d) Capsular fruits
41. Water potential and osmotic potential of pure water is
a) Zero and zero
b) 100 and zero
c) 100 and 100
d) Zero and 100
42. When pea seeds and wheat seeds are put in water, which of the two will imbibe more water?
a) Wheat seeds
b) Pea seeds
c) Both will imbibe equal amount of water
d) Pea seeds imbibe water only at alkaline pH
43. Nyctinasty and seismonasty in plants like bean and touch me not are produced due to
a) Reversible osmotic potential in the cells
b) Reversible turgor pressure in the cell of their pulvini
c) Due to less pressure potential in the cells
d) Presence of less turgidity in the cells
44. Following statements are related with the diffusion of coloured molecules across a membrane. Select the correct statement, which shows the fastest rate of diffusion?
a) An internal concentration of 15% and external concentration of 10%
b) An internal concentration of 25% and external concentration of 50%
c) An internal concentration of 50% and external concentration of 25%
d) Both (b) and (c) shows fastest rate of diffusion
45. Choose the false statement
a) If bark of tree is girdled from main stem, the plant dies because ascent of sap is stopped
b) If xylem is girdled from main stem, wilting of leaves tales place
c) In the flowerering plant food is transported in the form of dissacharide sucrose
d) In Girdling experiment, in a plant, root dies first
46. Sunken stomata is found in the leaves of
a) Trifolium
b) Lemma
c) Nerium
d) Lilium
47. Who proposed cohesion theory of water movement in plants?
a) JC Bose
b) Priestly
c) Dixon and Jolly
d) TV Englemann
48. Study the following picture and the statements given below and choose the correct option

I. The above diagram shows the net movement of water from the dilute to concentrated solution
II. The two solutions are separated by a differentially permeable membrane
III. Water molecule strikes the membrane randomly on both the sides and pass through the same
IV. Diffusion of water does not occur from its lower chemical potential to higher chemical potential
a) I, II, III and IV
b) I, II and III
c) I, II and IV
d) I and IV
49. Read the following statements and choose the correct option given below
I. Major account of transpiration takes places through surface/margin of leaves
II. A little amount of water is lost through stem, this is reffered to cauline transpiration
III. Transpiration is comparatively a slow process then evaporation
IV. Transpiration driven ascent of sap does not depend on cohesion, adhesion and surface tension properties of water
a) I, II, III and IV
b) I, III and II
c) I, II and IV
d) II, III and IV
50. Direction of translocation of organic food or solutes, is
a) Upward
b) Downward
c) Radial
d) All of these
Answers
Solutions
26 (c)
The solution whose osmotic concentration (solute potential) is equal to that of another solution is called isotonic solution.
27 (c)
Plants obtain most of their carbon and oxygen from CO_2 present in the atmosphere
28 (a)
When plant cell is kept in saline water, exosmosis takes place, as a result of which cell decreases in size.
29 (a)
When carrier proteins allow two type of molecular movements together, it is termed as co-transport. It can be further divided into two types; symport and antiport. In symport process, two types of material are diffused in same direction
30 (b)
In 1980, Julius von Sachs, a German botanist, demonstrated for the first time that plants could be grown to maturity in a defined nutrient solution in complete absence of soil. This technique of growing plants in a nutrient solution is known as hydroponics. These methods require purified water and mineral nutrient salts.
31 (c)
It is because of the close packing of water molecules in the inter spaces and over the surface of the imbibant particles
32 (a)
In rooted plants, transport of inorganic substances like water and minerals occur by xylem and it is unidirectional in case of water
33 (a)
Guttation is loss of water in liquid form from uninjured part in plants. This water loss occurs through hydathodes or water stomata. Guttation usually occurs from tips and margins of leaves during early morning when there is high atmospheric humidity as during wet reasons. Water stomata or hydathodes are permanently opened pores.
34 (c)
Imbibition is a special type of diffusion when water is absorbed by solids colloids causing them to enormously increase in volume. The classical examples of imbibitions are absorption of water by seeds and dry wood.
35 (a)
A-Final level B-Dotpin
C-Initial level D-Sugar solution
E-Potato tuber
36 (b)
Transport of water and mineral in xylem is unidirectional and sap move upwards due to transpirational pull. While transport in phloem is bidirectional and multidirectional, transport of organic food by phloem takes place from the source to sink
37 (b)
The rate of transpiration can be reduced by using anti-transpirants. These can be used in two ways
- Metabolic inhibitors: PMA, ABA, aspirin
- Film forming antitranspirant: Silicon, low viscosity, waxes.
38 (d)
Statoliths are microscopic particles. According to statolith theory given by Haberlandt and Nemec (1900), the change in position of statoliths under the influence of gravitation causes differential growth.
39 (c)
In a plasmolysed cell, the space between nucleus and plasma membrane is occupied by isotonic solution.
40 (a)
Sugarcane (saccharum officinarum) is a monocot plant of family-Poaceae. In gases (Poaceae), the guard cells are dumb bell-shaped and their cell walls are thickened only in the middle.
41 (a)
The water potential and osmotic potential of pure water is zero
42 (b)
Proteins have a very high imbibing capacity, starch less and cellulose least. This is why the proteinaceous seeds, e.g., pea seeds will show more imbibiton than those of wheat seeds.
43 (b)
Turgor pressure causes movements
44 (d)
Diffusion process takes place between concentration of molecule solution and it is process, where the movement of molecules occur from a higher concentration to lower concentration, either it is internal or external. Higher the concentration gradient, higher will be the rate of diffusion
45 (a)
In a ringing or Girding experiment, the ring of bark, along with phloem is cut from the stem to represent the path of organic nutrients by phloem tissue. If phloem is not removed along with bark, supply of organic food will be continue and plant will survive. It xylem is girdled from main stem, supply of minerals and salts is stopped in the leaves and upper part of girdling site.
So, wilting of leaves takes place after sometimes. In girdling experiment, root dies first as supply of food is stopped. In flowering plant, sieve tube transport food in the form of disaccaharides (sucrose)
46 (c)
Generally, stomata are provided for water loss but plants, which grow in xeric habitat have sunken type of stomata in their lower epidermis of leaves to minimize the loss of water, e.g., Nerium.
47 (c)
Cohesion tension theory was proposed by Henry Dixon and Jolly in 1894. It is greatly supported and elaborated by Dixon (1914, 1924). It is also called as transpiration pull theory and is based on the following assumptions
1. Cohesive and adhesive properties of water molecules
2. Continuous water column from root hairs through stem to tip of leaves
3. Strong transpiration pull exerted by all the transpiring leaves on the stem
48 (c)
The given diagram represents the process of osmosis. i.e., the movement of water from its higher concentration to lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane
49 (b)
An account of 90% total transpiration occurs through leaves, i.e., foliar. Remaining 10% takes place through stem, flower and fruits etc. Cauline transpiration is the loss of water from stem. Ascent of sap in conducting tissues of plant is affected by cohesion, adhesion and properties of water
50 (d)
The food material synthesizes in leaves of green plants and from seed during germination is translocated to growing regions and storage organs of plant.
That is all for this article. If you have any querries you can comment below.
